Bone marrow Biopsy
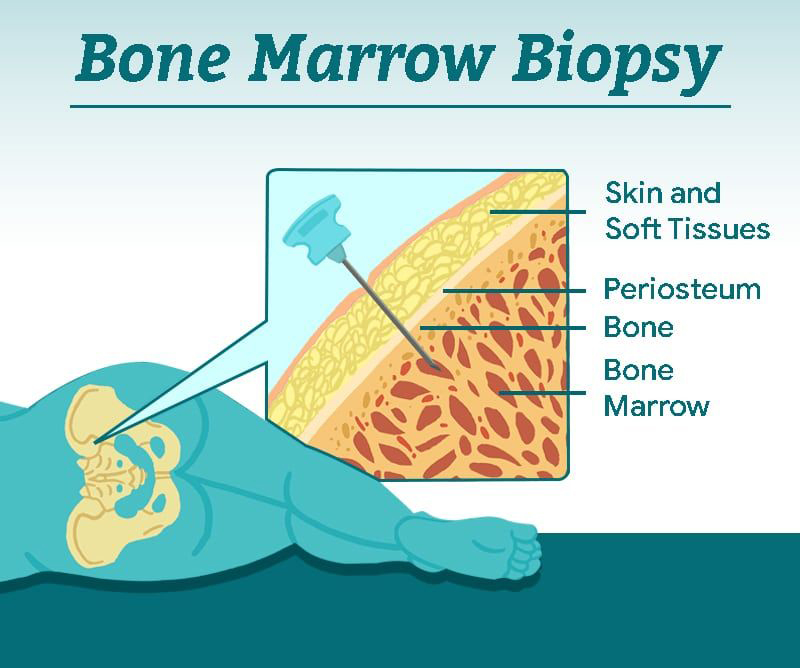
Bone marrow biopsy (BMB) FAQs! Ever wondered what it's all about? Keep reading... 👀 What makes up a BMB? Usually it includes 2 samples - the aspirate (liquid marrow 🩸) and the trephine (bone core 🦴) Why do we need 2 samples? The aspirate allows us to individually look at each BM cell under the microscope 🔬 (e.g. WBCs, RBCs) and classify them via flow cytometry (a method of identifying and measuring pathological cells using their surface markers e.g. CD19 for B-cells) The trephine lets us look at the way the BM is organised and assess for things like fibrosis and infiltration. We can also apply stains 🖌 (immunohistochemistry) to detect specific cells on the trephine How is it done? It is a quick (20-30 min) awake procedure using local anaesthetic. It does not require a theatre and is often done at the patient bedside. It is done aseptically using 2 separate needles 💉 (aspirate and trephine). Where do you take the samples from? Most times we manage to get samples from the pos...





